
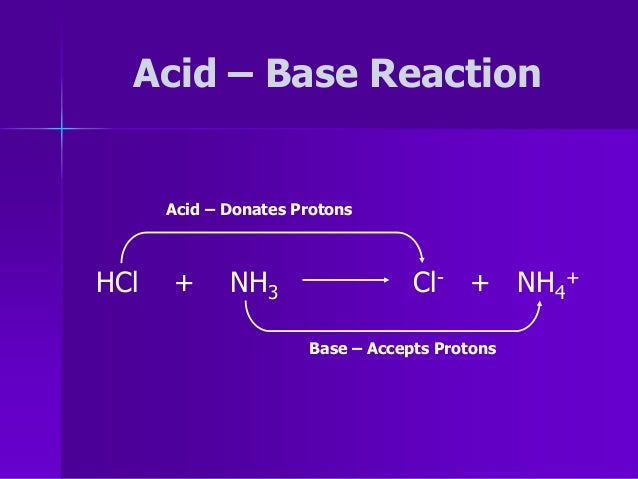
The accompanying figure shows another medication (lidocaine) as a hydrochloride salt. Dextromethorphan, an ingredient in many cough medicines, is dispensed as dextromethorphan hydrobromide. Hydrobromic acid, for example, gives hydrobromide salts. Acids other than hydrochloric acid are also used. Examples include the powerful painkiller codeine, which is commonly administered as codeine hydrochloride. Drugs that are modified in this way are called hydrochloride salts. The label (sl aq) means “slightly aqueous,” indicating that the compound RN is only slightly soluble. The modified drug molecules can then be isolated as chloride salts: where RN represents some organic compound containing nitrogen. The nitrogen atoms-acting as Brønsted-Lowry bases-accept the hydrogen ions from the acid to make an ion, which is usually much more soluble in water. Fortunately, those drugs that contain proton-accepting nitrogen atoms (and there are a lot of them) can be reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid. However, many complex organic compounds are not soluble or are only slightly soluble in water. For example, drugs often need to be water soluble for maximum effectiveness. To Your Health: Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Reactions in Pharmaceuticals There are many interesting applications of Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reactions in the pharmaceutical industry.

Why oxidizing agent is reduced?Īn element that is oxidized is a reducing agent, because the element loses electrons, and an element that is reduced is an oxidizing agent, because the element gains electrons. Respiration is exergonic because energy is released when large high-energy molecules (glucose) are broken down into smaller molecules. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Hydrochloric-Acid-58e7b8423df78c51624ea679.jpg)
Hcl acid or base free#
As shown below, the overall reaction is exergonic the free energy change for the reaction is -4 Kcal per mole of G-6-P synthesized. Reaction 1: In the first reaction of glycolysis, the enzyme hexokinase rapidly phosphorylates glucose entering the cell, forming glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P). Why is glycolysis an exergonic process?Ī. It releases the energy that is stored in the 2 molecules of pyruvate. The Krebs cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules. Most of the energy is conserved in the high-energy electrons of NADH and in the phosphate bonds of ATP. Glucose is oxidized into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid in an exergonic reaction.
As a result, a transthylakoid proton gradient (ΔpH) is generated, leading to the production of ATP without concomitant production of NADPH, thus increasing the ATP/NADPH ratio within the chloroplast. In cyclic electron flow (CEF), electrons are recycled around photosystem I. Thus, -NO2 is very good at pulling electrons away. It can do this by both resonance (double bond shifts away from C=C to become C=N) and by the inductive effect. Why is nh2 inductive effect?Īlso, due to the positive charge, it will be unstable, and the nitrogen will try to pull electrons away from the ring to reduce the positive charge. HCl is a strong acid because it dissociates almost completely. When HCl molecules dissolve they dissociate into H+ ions and Cl- ions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
